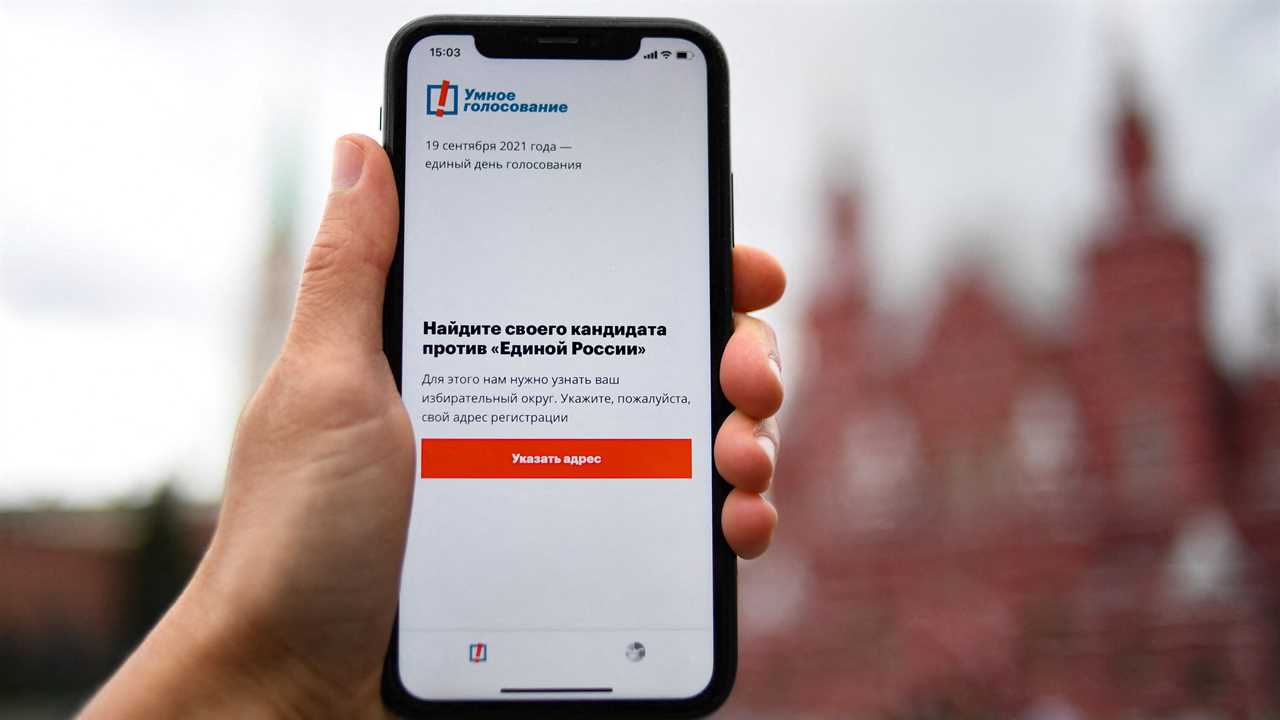
MOSCOW — An app designed by Russian activists to coordinate protest voting in this weekend’s elections disappeared from the Google and Apple app stores in the country on Friday, a major blow to the opposition leader Aleksei A. Navalny and allies who hoped to subvert the commanding position of President Vladimir V. Putin’s governing party.
Google removed the app Friday morning after the Russian authorities issued a direct threat of criminal prosecution against the company’s staff in the country, naming specific individuals, according to a person familiar with the company’s decision. The move comes one day after a Russian lawmaker raised the prospect of retribution against employees of the two technology companies, saying they would be “punished.”
The person declined to be identified for fear of angering the Russian government.
On Friday Mr. Putin’s spokesman, Dmitri S. Peskov, said, “That app is illegal” when asked about it on his regular call with journalists. “Both platforms have been notified and in accordance with the law they made these decisions, as it seems,’’ he said.
Apple did not respond to requests for comment about the availability of the Navalny app in its store.
The app disappeared just as voting got underway in the three-day parliamentary election, in which Mr. Navalny’s team was hoping to use its app — called “Navalny” — to consolidate the opposition vote in each of Russia’s 225 electoral districts.
“Removing the Navalny app from stores is a shameful act of political censorship,” an aide to Mr. Navalny, Ivan Zhdanov, said on Twitter. “Russia’s authoritarian government and propaganda will be thrilled.”
Maintaining open, uncensored access to their services, especially in authoritarian countries, is becoming one of the most vexing challenges for American tech companies like Apple, Google, Facebook and Twitter. In countries such as India, Myanmar and Turkey, the authorities are increasingly pressuring the companies to censor certain political speech, or ordering internet outages to block access to the web.
Civil society groups have warned that forcing the companies to conform to a patchwork of laws and regulations risks creating a more fractured internet, where the products and services available to people will depend on where they are.
The threat to prosecute local employees is an escalation by the Kremlin as it seeks to induce Western tech giants to fall in line with a broader internet crackdown. The country’s internet regulator, Roskomnadzor, has repeatedly demanded that the companies remove certain content, on pain of fines or restrictions on access to their products. The government says that American internet companies are meddling in Russia’s domestic affairs by allowing anti-Kremlin activists to use their platforms freely; Mr. Navalny’s movement was outlawed as extremist this summer.
The Russian government had been increasingly blunt in recent days about its willingness to use threats to prevent the use of the app. “With the participation of Apple and Google, specific crimes are being committed, the scale of which may only increase in the coming days,” Vladimir Dzhabarov, a member of Russia’s upper house of Parliament, said on Thursday. “Individuals contributing to their parent companies’ evasion of responsibility on the territory of the Russian Federation will be punished.”
Bailiffs visited Google’s offices earlier this week seeking to enforce court-ordered measures against the protest voting campaign, state media reported.
Russian authorities have been pressuring Apple and Google for weeks to remove the Navalny team’s voting app. With Mr. Navalny’s websites blocked inside Russia, the app became a loophole allowing exiled allies of the imprisoned politician to continue to reach a wide audience. Nearly every smartphone runs Apple’s iOS or Google’s Android operating system, making their app stores the key artery for getting any product to the public.
The Russian Foreign Ministry summoned the American ambassador to Moscow, John J. Sullivan, last week and announced that “American ‘digital giants’” had broken Russian law “in the context of the preparation and conduct of the elections.”
“The patience of the Russian side, which for now has refrained from putting up barriers to American business in Russia, is not unlimited,” the Foreign Ministry’s spokeswoman, Maria V. Zakharova, warned on Thursday.
The “Navalny” app is central to a protest-vote strategy that the opposition leader calls “smart voting.” Elections in Russia are not free and fair, but the Kremlin still seeks the sheen of popular legitimacy by holding elections in which a stable of dull parties typically splits the opposition vote.
The Navalny strategy, first deployed regionally in 2019, seeks to turn that system of “managed democracy” against Mr. Putin. The goal is to defeat as many candidates representing the governing United Russia party as possible by having all opposition-minded voters in each district pick the same challenger — whether or not they agree with their views. The “Navalny” app coordinates the process, requesting a user’s address and responding with the name of the candidate they should vote for.
The Navalny team on Friday said they would seek to get the names of their “smart voting” picks out by alternate methods, such as automated responses in the messaging app Telegram. But they voiced anger at Apple and Google for apparently folding to Kremlin pressure.
“This shameful day will long remain in history,” Leonid Volkov, Mr. Navalny’s longtime chief of staff, wrote on his Telegram account.
Anton Troianovski reported from Moscow, and Adam Satariano from London. Oleg Matsnev and Ivan Nechepurenko contributed reporting from Moscow.






