The U.S. economy faces turbulent times
The U.S. economy has been facing turbulent times lately, with the U.S. personal consumption expenditure (PCE) inflation index rising by a significant 3.5% over the past 12 months. Even when excluding the volatile food and energy sectors, it's evident that the efforts made by the U.S. Federal Reserve to curb inflation have fallen short of their 2% target rate.
Investors question Bitcoin's resilience
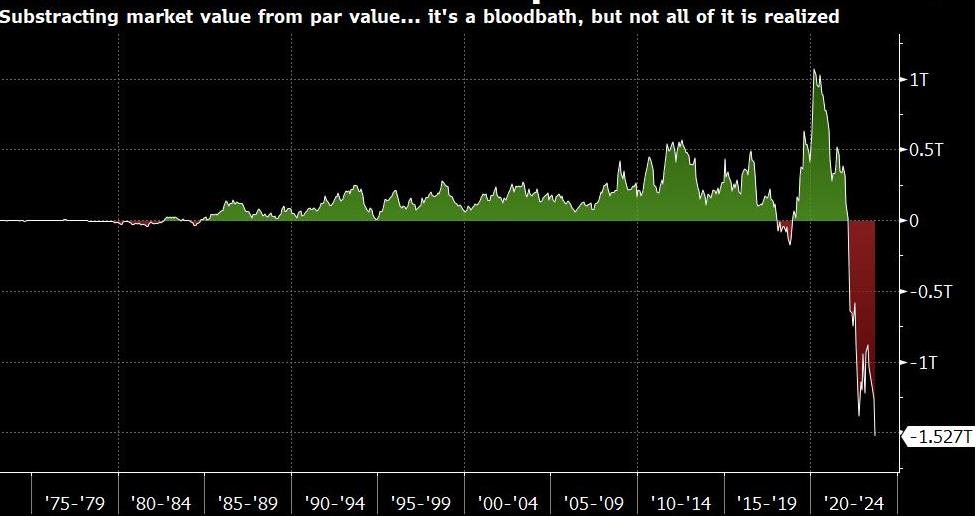
U.S. Treasuries have lost a staggering $1.5 trillion in value, primarily due to these rate hikes. This has led investors to question whether Bitcoin (BTC) and risk-on assets, including the stock market, will succumb to heightened interest rates and a monetary policy aimed at cooling economic growth.
The risk of financial instability
As Daniel Porto, the head of Deaglo London, pointed out, there is a real risk that rates could climb even higher, exacerbating the losses to fixed-income investors. An additional $8 trillion in government debt is expected to mature in the next 12 months, further contributing to financial instability.
The consequences of high interest rates
One of the primary drivers behind the recent turmoil in financial markets is the rise in interest rates. As rates increase, the prices of existing bonds fall, a phenomenon known as interest rate risk or duration. This risk isn't limited to specific groups; it affects countries, banks, companies, individuals and anyone holding fixed-income instruments.
Banks at risk
Banks, which typically borrow short-term instruments and lend for the long-term, are especially vulnerable in this environment. They rely on deposits and often hold Treasuries as reserve assets. When Treasuries lose value, banks may find themselves short of the necessary funds to meet withdrawal requests. This compels them to sell U.S. Treasuries and other assets, pushing them dangerously close to insolvency and requiring rescue by institutions like the FDIC or larger banks. The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), First Republic Bank, and Signature Bank serves as a warning of the financial system instability.
The Federal Reserve's limited intervention
While emergency mechanisms can provide relief, such as the Federal Reserve's BTFP emergency loan program, these measures do not make the losses disappear. Banks are increasingly offloading their holdings to private credit and hedge funds, flooding these sectors with rate-sensitive assets. This trend is poised to worsen if the debt ceiling is increased to avoid a government shutdown, further raising yields and amplifying losses in the fixed-income markets.
Bitcoin's potential as an inflation hedge
As long as interest rates remain high, the risk of financial instability grows, prompting the Federal Reserve to support the financial system using emergency credit lines. That is highly beneficial for scarce assets like Bitcoin, given the increasing inflation and the worsening profile of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet as measured by the $1.5 trillion paper losses in U.S Treasuries. There’s hardly a scenario where one would be pessimistic with Bitcoin under those circumstances.
Note: This article is for general information purposes and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal or investment advice. The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed here are the author’s alone and do not necessarily reflect or represent the views and opinions of Cointelegraph.
Did you miss our previous article...
https://trendinginthenews.com/crypto-currency/pond0x-decentralized-exchange-surpasses-100-million-in-trading-volume






